3D data measurement
Enables dimensional measurement and mapping of structures through 3D photogrammetry
An advanced measurement system, which can be described as an evolution of 3D photogrammetry systems, is utilized in a wide range of fields including measurement and surveying, as well as for investigation and research purposes.
By analyzing the 3D coordinates (X, Y, Z) of subjects from two or more images (photos) captured with a digital camera, it is possible to convert natural objects and structures into 3D data, enabling the measurement of dimensions and areas, as well as mapping.
It simplifies 3D conversion and streamlines the workflow
By obtaining 3D coordinate data from two digital camera images, measurement and mapping are possible.
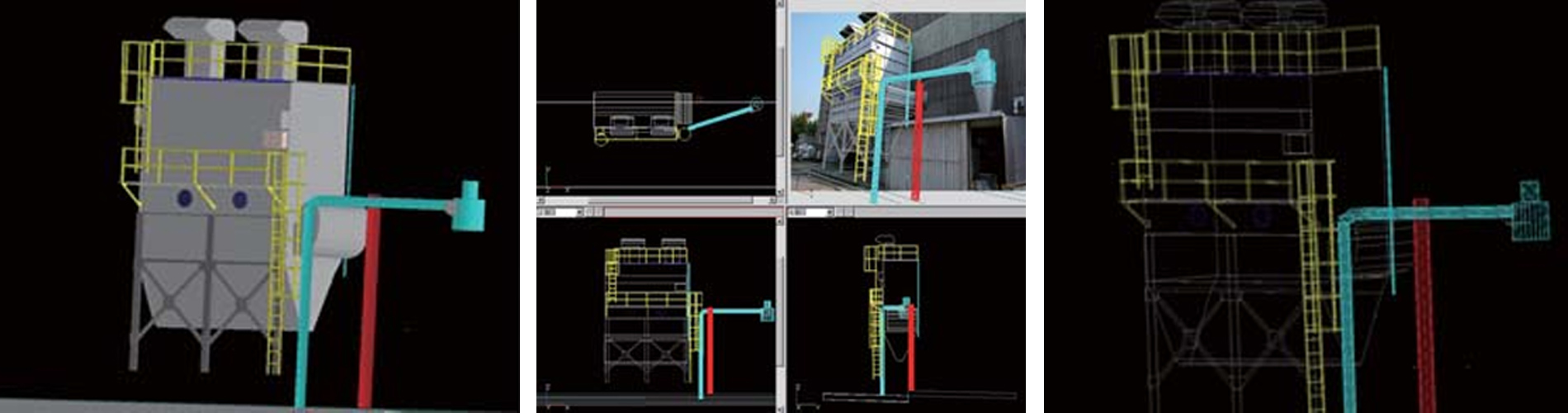
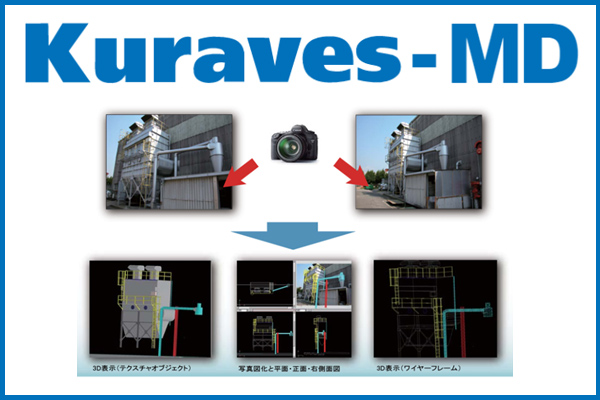
[Utilization technology] Kuraves-MD
The measurement results of the subject are created as 3D data, enabling the measurement of the length, area, and volume of structures, the creation of cross-sectional drawings, angle calculations, and more. Additionally, it allows for composite displays and further drawing by importing 3D CAD data.
Regarding the photography of source images
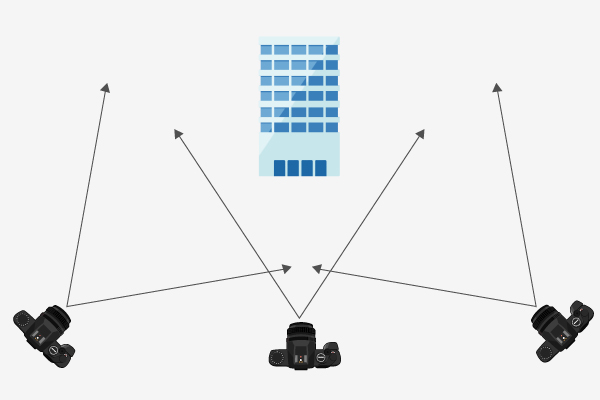
For the photographs used, images of the subject taken from different positions are generally required. As shown in the left figure, the angles of view need to be different. Therefore, depending on the location conditions, this can sometimes be difficult.
The applications, such as analysis and drawing creation, are diverse.
- Measurement and analysis are possible both indoors and outdoors.
Analysis is possible even at distances of over 100m from the subject of measurement, as well as with close-up photography at 1m. - It can be utilized in sites or facilities where manual measurement is not feasible.
With the captured photographs, additional analysis is possible even if there are measurement omissions in challenging measurement sites. - It's possible to create diagrams of complex plant piping and generate data for presentations.
By using the separate 'Object Registration and Editing Tool' (sold separately) in conjunction, it enables laying out other CAD data onto site photo data, facilitating the creation of 3D models, floor plans, and elevations. - The volume measurement of objects and the creation of contour lines and cross-sectional diagrams.
By utilizing the separately sold 'Drawing Tool', it enables the creation of contour lines, vertical and horizontal cross-sectional diagrams, volume calculations, and more from analysis data. It also allows for the utilization of survey data.
Examples of field work applications that can be utilized
- USAGE -
In fields such as architecture, structural engineering, and civil engineering, it's possible to utilize it for tasks ranging from earthwork calculations to surveying. Since these can typically be based on image data captured with commercially available digital cameras (capable of shooting in M mode), the approach to these tasks is relatively straightforward.
Measurement and reverse engineering inside factory facilities
Three-dimensional measurement and visualization of factory equipment, machinery, structures, and plant piping.
Maintenance and upkeep
Piping, metal corrosion levels, tower height, distance between electrical wires and structures, angle measurements, and tool contact interference checks.
Inventory volume verification
Inventory levels of pulp, ore, lime, coke, rock salt, scrap, etc., quarrying, and waste disposal sites.
Survey measurements
Road signs, dimensions of products from other companies, area of concrete spalling, presence of wire sagging, horizontal and vertical measurements.
Civil engineering and surveying
Slope collapse, landslides, construction planning, tracking of temporal changes, general civil engineering survey and design, archaeological and cultural heritage surveys, aerial photograph analysis.
Equipment inspection and planning
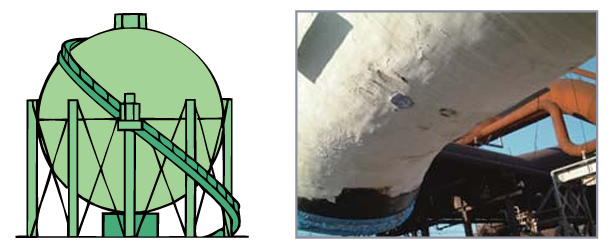
Measurement of metal corrosion areas
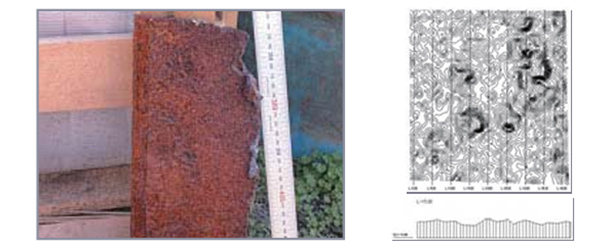
Digitization of structures
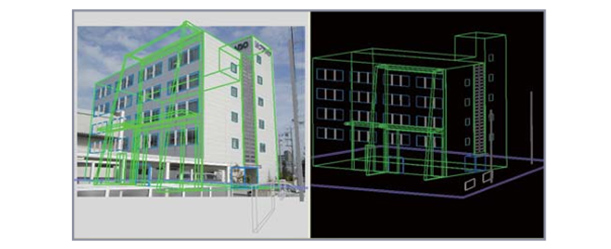
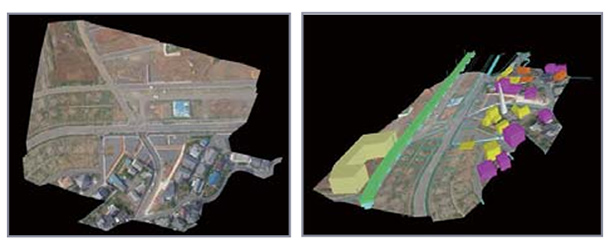
3D modeling from aerial photographs
Workflow from data collection to data creation
- FLOW OF DATA CREATION -
- [Preparation] Camera calibration and photography
- [Software operation] Allocation of initial control points and camera position calculation
- [Software operation] Correspondence point setting
- [Software operation] Automated extraction and allocation of arbitrary coordinate points
- [Software operation] 3D data creation and object visualization
- [Software operation] Cross-sectional drawing, contour lines, volume measurement, input of planned data
