Rebar detection: electromagnetic radar method
Non-destructive inspection of reinforcing bars inside concrete
Rebar investigation involves examining the rebar present inside concrete structures. This investigation is conducted using a specialized non-destructive inspection device called a rebar detector. With this device, one can measure the rebar arrangement, concrete cover thickness, and the position of pipes, among other things. Rebar investigation is essential to prevent the cutting or damage of internal rebar and other components when repairing or renovating existing concrete structures.

Rebar investigation using an electromagnetic radar scanner
There are two methods for conducting rebar investigation: the electromagnetic radar method and the electromagnetic induction method. The electromagnetic radar method involves emitting radar waves (pulse waves) from an antenna located at the bottom of the rebar detector. These radar waves reflect off objects such as rebar and return to the detector, which then displays the position of the rebar. Compared to X-ray inspection, this method is safer and more cost-effective, making it widely used.
The electromagnetic induction method involves conducting tests by placing the investigation target within a magnetic field generated by passing alternating current through a coil. Compared to the electromagnetic radar method, it allows for higher accuracy measurements. However, it cannot measure deep concrete cover thickness or detect objects other than rebar, such as PVC pipes or voids.
At Sugitec, we primarily conduct inspections using rebar detectors that utilize the electromagnetic radar method.
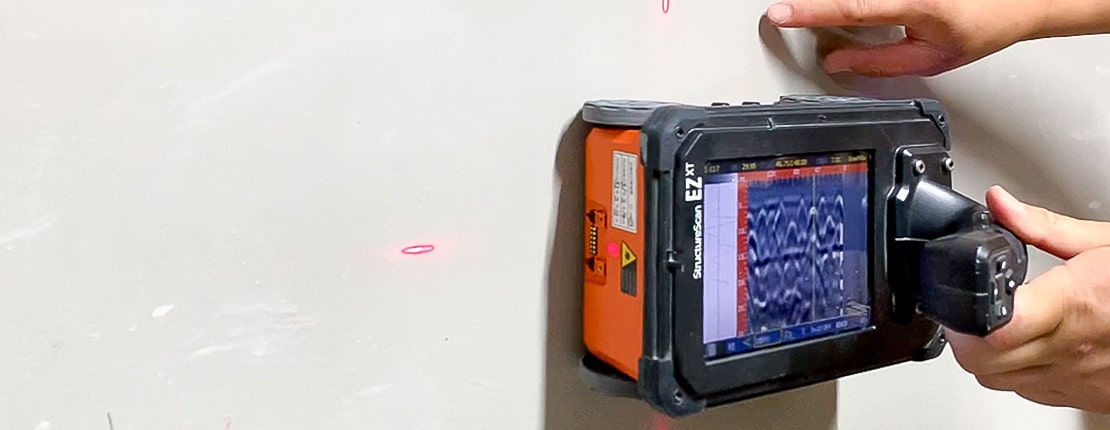
Investigation using an electromagnetic radar scanner
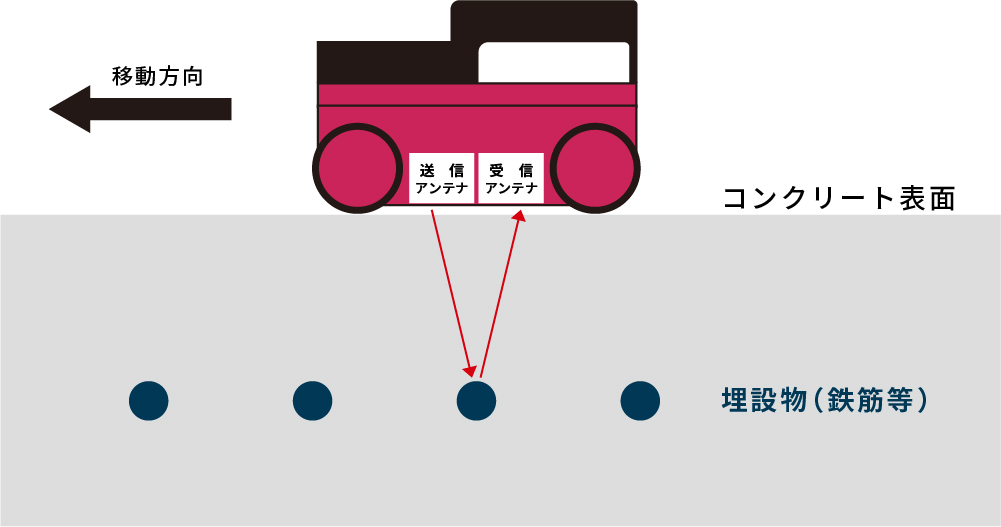
The mechanism of the electromagnetic radar scanner is illustrated as follows. First, radar waves are emitted into the concrete from the 'transmitting antenna' located on the bottom surface of the electromagnetic radar scanner.
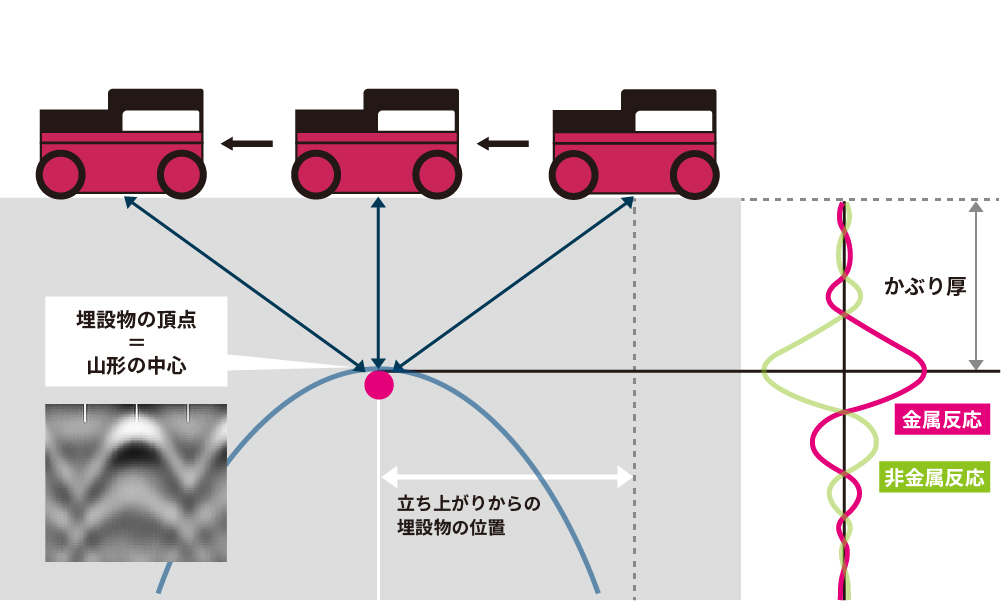
Radar waves are reflected when they encounter embedded objects inside the concrete, and these reflections are received by the receiving antenna. The system detects the distance to the embedded object based on the time it takes for the radar waves to be emitted and then return.
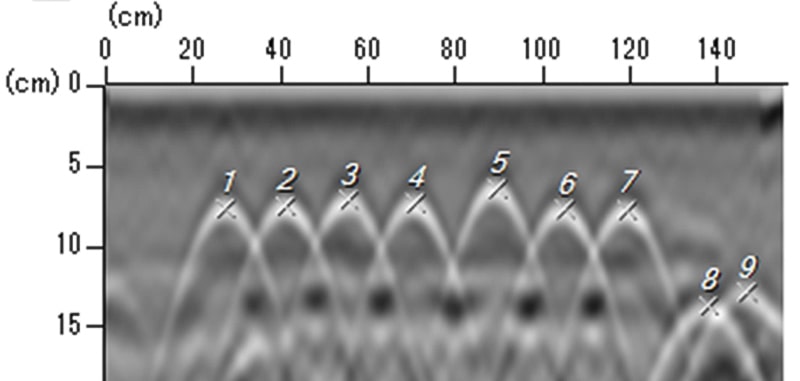
Example of images measured by the rebar detector
Electromagnetic radar scanner primarily in use

An advanced rebar detector that utilizes a smartphone as its display, enabling various functionalities
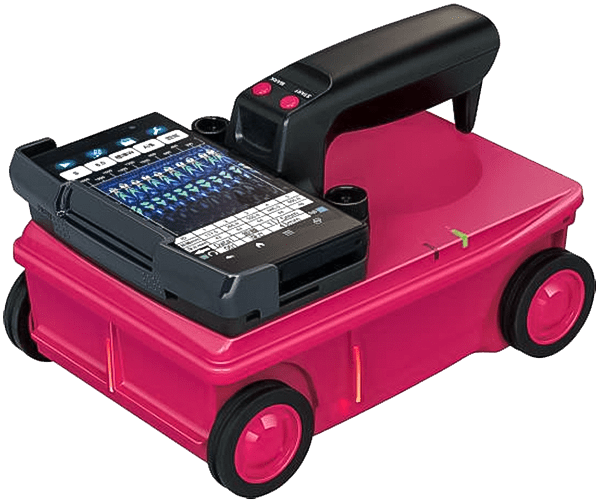
[Handy search] NJJ-200K-3D
A handheld rebar detector with the smallest and lightest compact body, equipped with cutting-edge technology. It allows for easy on-site 3D visualization of embedment conditions. Complex piping, W-rebars, and staggered rebar patterns, which are difficult to discern in cross-sectional images, can be easily identified. Additionally, by using a smartphone as the display, it enables various rebar detection capabilities that were previously impossible with conventional devices.
- Concrete internal investigation depth: approximately 60 cm
- Relative permittivity setting range: 2 to 20
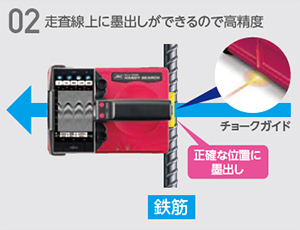
Fast, Easy, and High-Precision Layout
We have adopted a system that allows for high-precision layout along scanning lines, and since it does not traverse back and forth along the scanning line, chalk guiding for layout can be done quickly and easily. As shown in the diagram below, layout can be completed in two steps, achieving time savings and improved accuracy.


On-site data verification is possible with the '3D visualization software' for measurement data
Measurement results can be displayed in 3D on smartphones and tablets. There is also a simple reporting feature that allows for immediate JPG output.
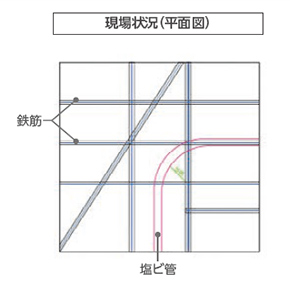
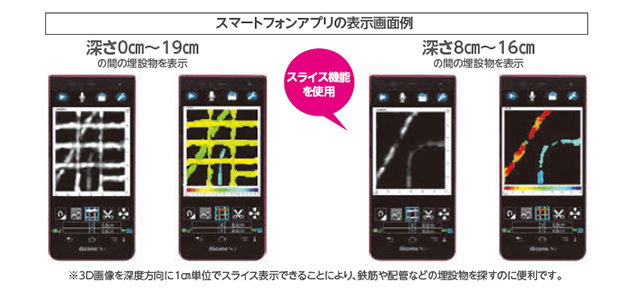
With an investigation depth of approximately 60 cm, it is possible to detect not only rebar but also non-metallic pipes, thickness, voids, cracks, and other features
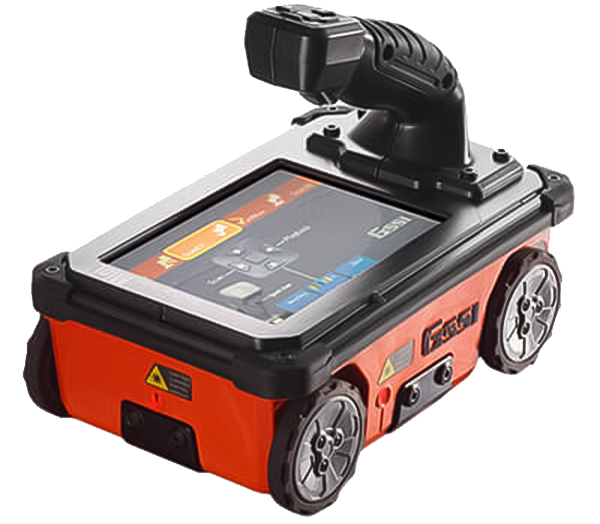
[Structure scan] SIR-EZ-XT
With high resolution, deep penetration, and multifunctionality, it is suitable for use in various environments. It can be used not only for rebar detection but also for detecting non-metallic pipes, thickness, voids, cracks, soil contamination, and more (including W-rebar detection)
- Concrete internal investigation depth: approximately 60 cm
- Relative permittivity setting range: 2 to 20

Achieving high resolution and deep penetration with high frequency. Versatile and multifunctional for various applications
The world's first concrete explorer with software and hardware version-up capability. The only exploration machine that continues to evolve. Can be used not only as a rebar probe, but also as a probe for non-metallic pipes, thickness, cavities, cracks, and soil erosion.



Conduit Pipe Discrimination Unit for immediate detection of live wires
By attaching it to the front of the structure scanner, it can immediately search for active wires (wires with current flowing through them), preventing wire cutting accidents before they occur. The signal from an active wire is indicated by a light blue (green) line on the search screen as shown in the figure below, and a mountain waveform that matches the peak value is determined to be an active conduit.

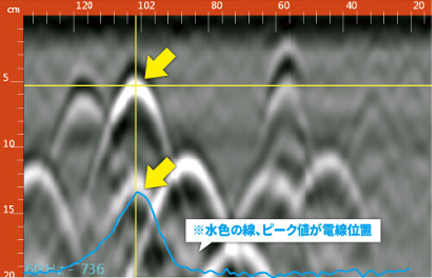
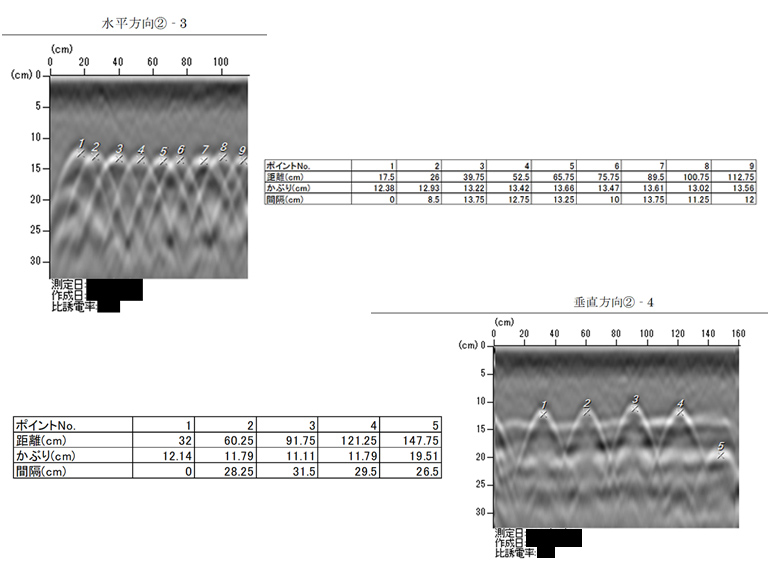
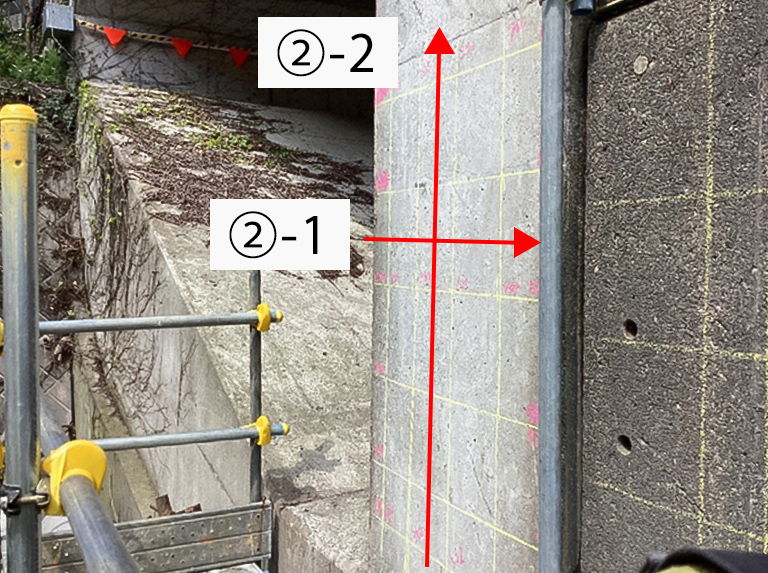
Rebar exploration Measurement example: A certain bridge abutment
- REBAR EXPLORATION -
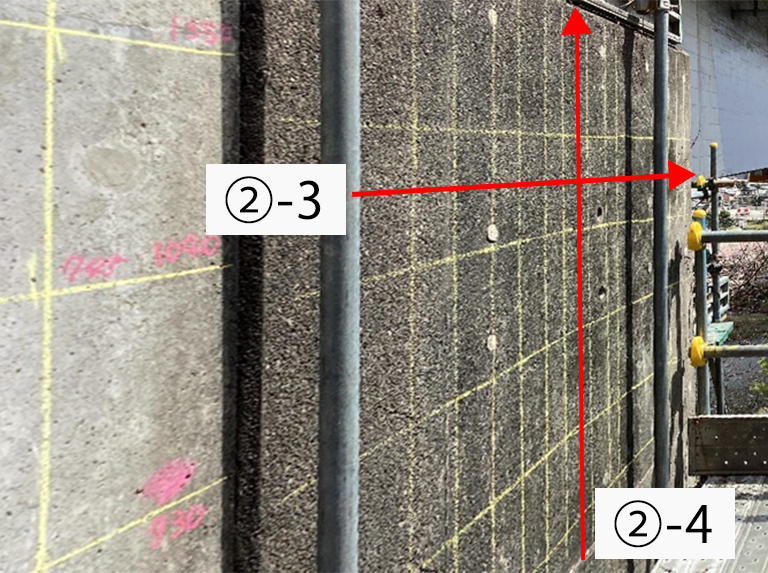
Example: Side Marking of Bridge Abutment
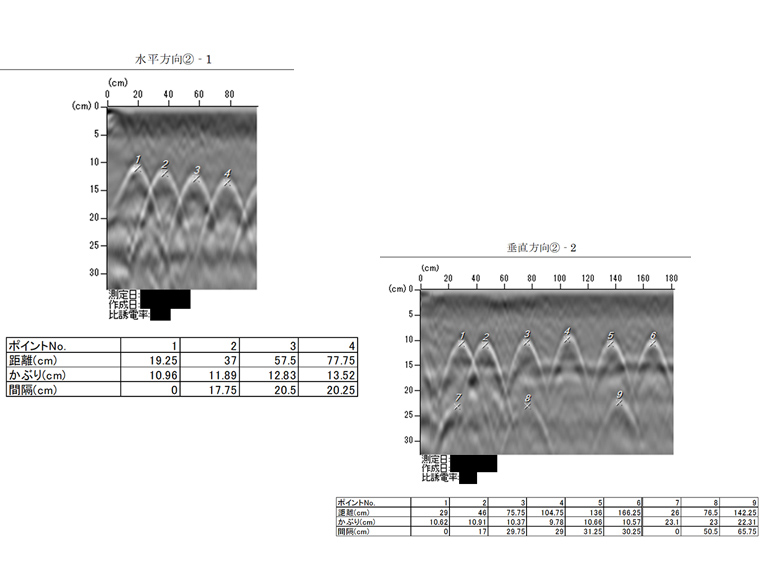
Rebar Detector Radar Waveform
Example:Bridge Pier Layout

Rebar Detector Radar Waveform