Smart Crack Checker
Improving traditional survey methods prone to human error
In traditional crack surveys of concrete structures conducted manually, there is a high potential for human error, such as omissions in field notes. Surveys of large areas, such as logistics facilities, require enormous amounts of time and cost. Although commercial software for crack surveys is available, it requires semi-automated analysis, necessitating manual stitching of continuous photos taken at each site. Additionally, it is necessary to establish a method for capturing continuous photos of floor surfaces.
To address these issues, we developed a method for efficiently capturing continuous photos of floor surfaces and a system where AI automatically detects cracks from orthophotos created by stitching together these continuous photos. This innovation prevents human error and significantly improves work efficiency.
Automatic Crack Detection with AI from Visible Images
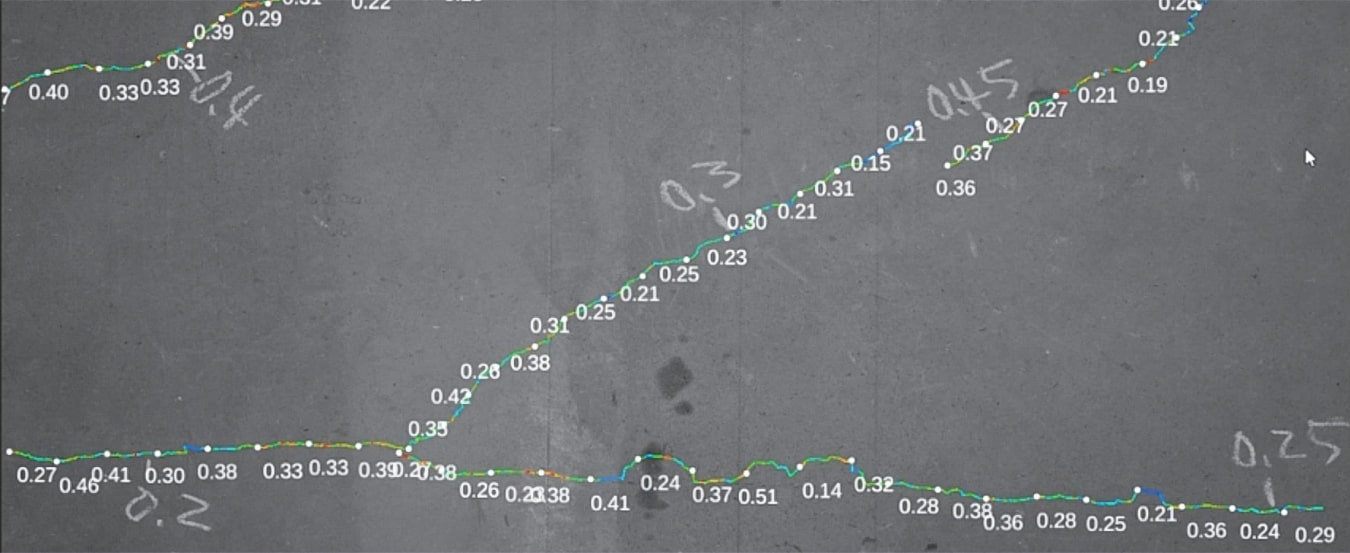
The Smart Crack Checker uses our proprietary 'Large Surface Imaging Technique' to efficiently capture a large number of visible images. These images are then automatically corrected and stitched together to generate orthophotos. From these orthophotos, the system traces crack locations, allowing for objective and automatic extraction of cracks. By leveraging AI, the system can accurately measure the width and length of cracks from the visible images.
Features of the Smart Crack Checker
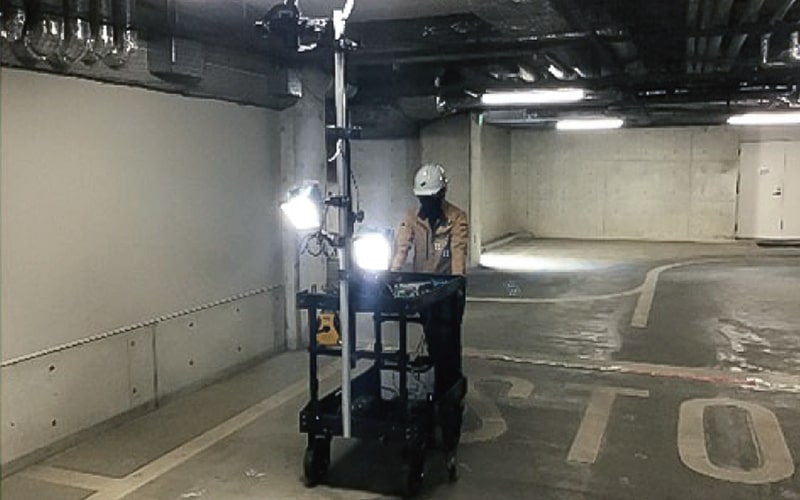

Large Surface Imaging Technique for Extensive Floor Areas
A mobile imaging unit that manages shooting positions by rows, obtaining images with the same correction values for each row, enabling automatic internal correction and synthesis. By utilizing this method, continuous photography of extensive concrete floor surfaces becomes feasible.
Image Calibration
Perspective Correction

During the initial stage of capturing images, calibration is conducted using the first image. Subsequent images captured are automatically corrected.
Automatic Image Stitching
Orthoimage Generation
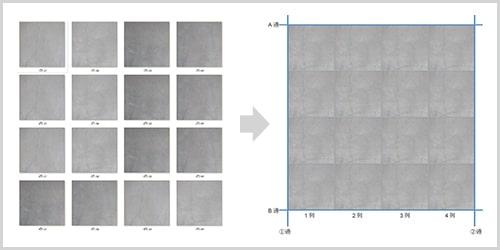
By automatically synthesizing the vast collection of captured images, we create an "orthoimage" which allows us to obtain a single wide-area image for crack detection.
The conventional survey method - this is...
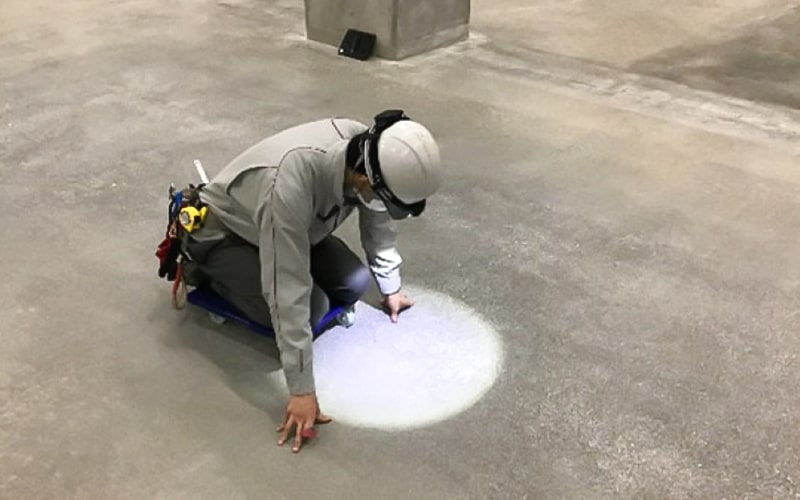

In the past, surveys were conducted manually using sketches, which posed the risk of human error such as missing entries. Additionally, for large-scale facilities like logistics centers, it consumed considerable time and cost.
This is how it used to be!
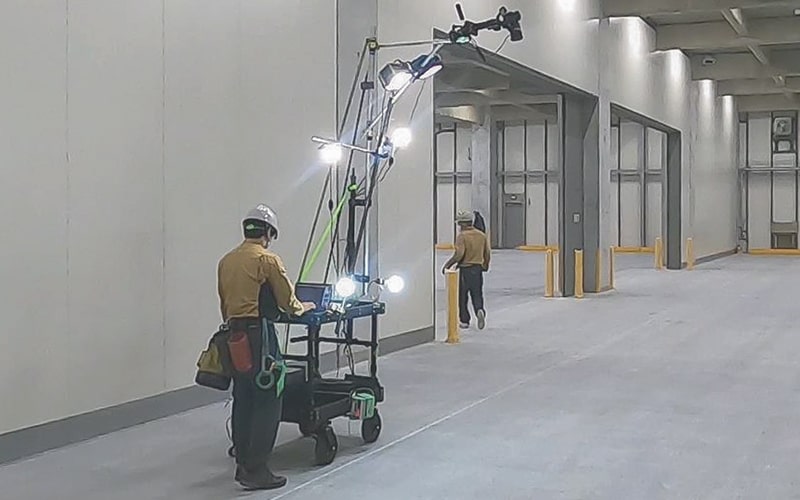

The 'Large Planar Imaging Technique' of the imaging unit enables continuous capturing of the floor surface. By stitching together the images taken for each column, a wide-area orthoimage is generated for analysis.
The AI-based detection algorithm coupled with automatic crack mapping functionality.
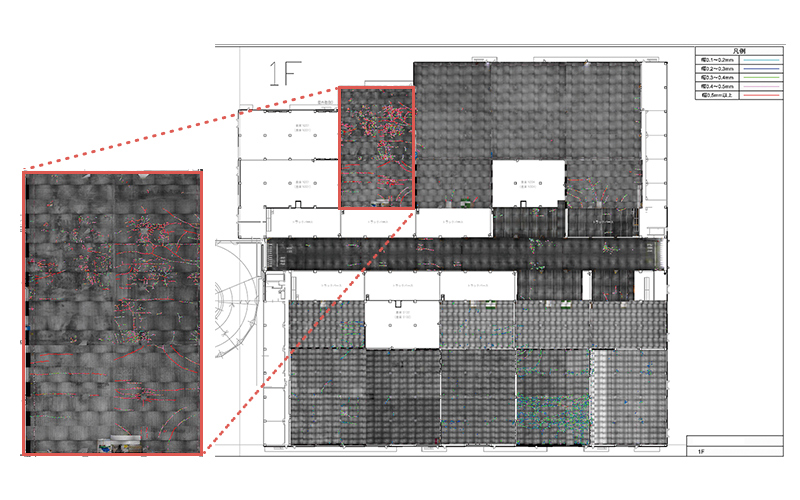
The AI detects curves indicative of potential cracks from the images, and based on that, predicts the crack width. Cracks are visualized and outputted with color-coding according to their width.
Detection and selection of crack widths, etc
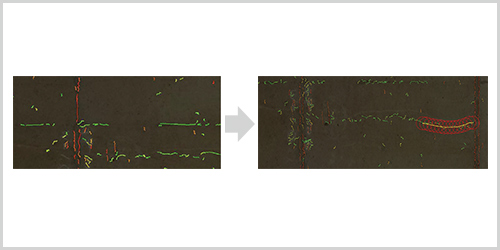
The system loads the synthesized image of the wide area on the PC and detects curves that may represent cracks on the screen. Cracks can be traced with the cursor to define their characteristics such as direction, length, width, and spatial relationship.
Analysis from Crack Width Candidates
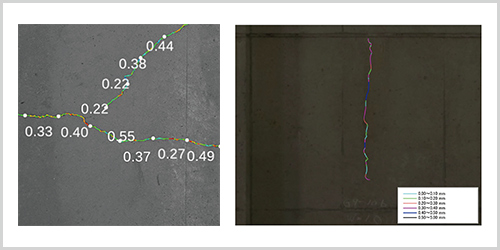
The system divides the image into regular intervals and displays color-coded representations based on crack width.
